COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION
• Functions: Voice of governments of EU countries, approve legislation and coordinate policies
• Members: Ministers of the governments of each EU country, depending on the scheduled
• President: the presidency is rotated by EU countries, for periods of 6 months
• Established in 1958 (as Council of the European Economic Community)
• Headquarters: Brussels (Belgium)
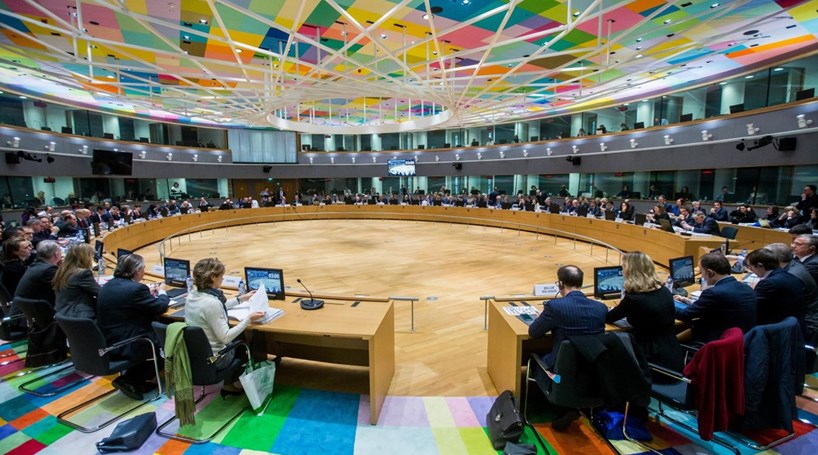
Ministers of the governments of each EU country meet in the Council to discuss, amend and enact legislation and coordinate policies. Ministers are empowered to enter into commitments on behalf of their governments on the measures adopted at the meetings.
The EU Council, together with the European Parliament, is the EU's main decision-making body.
Do not confuse this institution with:
The European Council - a quarterly summit bringing together the EU Heads of State and Government to lay the foundations of EU policy
The Council of Europe - is not an EU institution
What does the Council do?
Negotiates and adopts European legislation, together with the European Parliament, on the basis of proposals from the European Commission
Coordinates the policies of EU countries
Defines foreign and security policy, based on the guidelines of the European Council
Concludes agreements between the EU and other countries or international organizations
Approves the EU budget in conjunction with the European Parliament
Composition
The Council does not have fixed members, meeting with 10 different formations according to the scheduled political area. Each country sends a minister of guardianship of the area in question.
For example, when the Council meets to discuss economic and financial affairs (the ECOFIN Council), it is the Finance Minister of each country that will be present.
Who chairs the meetings
The Council in which the Foreign Ministers meet shall always be chaired by the High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy. Every other meetings of the Council are chaired by the competent Minister of the country holding the rotating presidency of the EU.
For example, any meeting of the Environment Council during the period in which Portugal takes over the Presidency is presided over by the Portuguese Minister responsible for the environment.
The consistency of the work is ensured by the General Affairs Council, which is supported by the Committee of Permanent Representatives, composed of the Permanent Representatives of the Member States to the EU, who have the status of ambassadors.
Eurozone countries
Eurozone countries coordinate their economic policies within the framework of the Eurogroup, which comprises the Ministers of Economy and Finance. The Eurogroup meets on the eve of ECOFIN Council meetings. The agreements reached at the meetings of the Eurogroup are the subject of an official decision at the ECOFIN Council the following day, being voted only by the ministers of the Eurogroup countries.
How does the Council work?
All debates and votes are public
To be approved, decisions generally require a qualified majority:
55% of the countries (currently with 28 EU countries, representing 16 countries) representing at least 65% of the total EU population
To block a decision, at least 4 countries (representing at least 35% of the total EU population) are needed.
Exception - sensitive issues such as foreign policy and taxation require unanimity (favorable votes from all countries)
The simple majority is sufficient when voting on procedural and administrative matters
The Council and the citizen
You can ask general questions to the Council's public information service.
Check here the website of the Council of the European Union